GENERAL MEDICINE CASE 3
- This is an online E log book to discuss our patient's de-identified health data shared after taking his/her/guardian's signed informed consent.
- Here we discuss our individual patient's problems through series of inputs from available global online community of experts with an aim to solve those patient's clinical problems with collective current best evidence based inputs.
- This E log book also reflects my patient-centered online learning portfolio and your valuable inputs on the comment box is welcome."
- Case: A 23yr old Auto driver with complaints of paraparesis
I've been given this case to solve in an attempt to understand the topic of "patient clinical data analysis" to develop my competency in reading and comprehending clinical data including history, clinical findings, investigations and come up with a diagnosis and treatment plan.
You can find the entire real patient clinical problem in this link here..
https://vaish7.blogspot.com/2020/05/medicine.html?m=1
Following is my analysis of this patient's problem:
Chief complaints of the patient:
The problems in order of priority I found are
1)weakness of bilateral lower limbs since 5 days
complaints of tingling and numbness
2)vomitings 5days back 3-4 episodes non projectile non bilious food particles is content.
3)when he got up for urination,suddenly he had a fall and got up with the help of father.
4)gluteal abscess since 5months
5)scrotal abscess since 20 days
Explanation of the above complaints in detail.
1-WEAKNESS OF LOWERLIMBS AND SUDDEN FALL
Onset:sudden in onset
Duration :since 5 days
Associated conditions :
- Tingling and numbness
- history of sudden fall while he got up for urination.
Possible diagnosis:
1)A sudden fall may be indicative of vascular cause probably due to stroke or ischemia or infarcts in the brain.
2)Weakness may be caused by any one of the following related to vascular system,muscle or nervous system.
If Artery related
As in case of peripheral artery disease and varicose veins there will be pain,leg skin atrophy,and claudication,telengectasia. As there are no signs of this artery are ruled out.
#if any blood vessel in the brain undergoes infarction then there is a chance of sudden stroke and paralysis of limbs.
If suspecting nervous system related?
May be it is related to nerves because from the history there is history of weakness tingling and numbers in the feet
To understand the nerve related issue A thorough CNS EXamination is done and following are results.
CNS-EXAMINATION
Cns conscious
speech-normal
cranial nerves intact.
MOTOR SYSTEM
Right. Left
Bulk: normal. Normal
Tone: ul. normal. Normal
LL. hypotonia hypotonia
Power rt. lt
ul. 5/5. 5/5
LL. 2/5. 0/5
Reflexes.
Superficial reflexes
Right. Left
Corneal. P P
Conjunctival P. P
Abdominal. P. P
Plantar Extensor Extensor
Deep tendon reflexes
Right. Left
Biceps. 2+ 1+
Triceps. 2+ 1+
Supinator. 3+ 2+
Knee 3+ 2+
Ankle. 3+ 2+
jaw jerk. 1+. 1+
ankle clonus present. absent
Primitive reflex -absent
Involuntary movements - absent
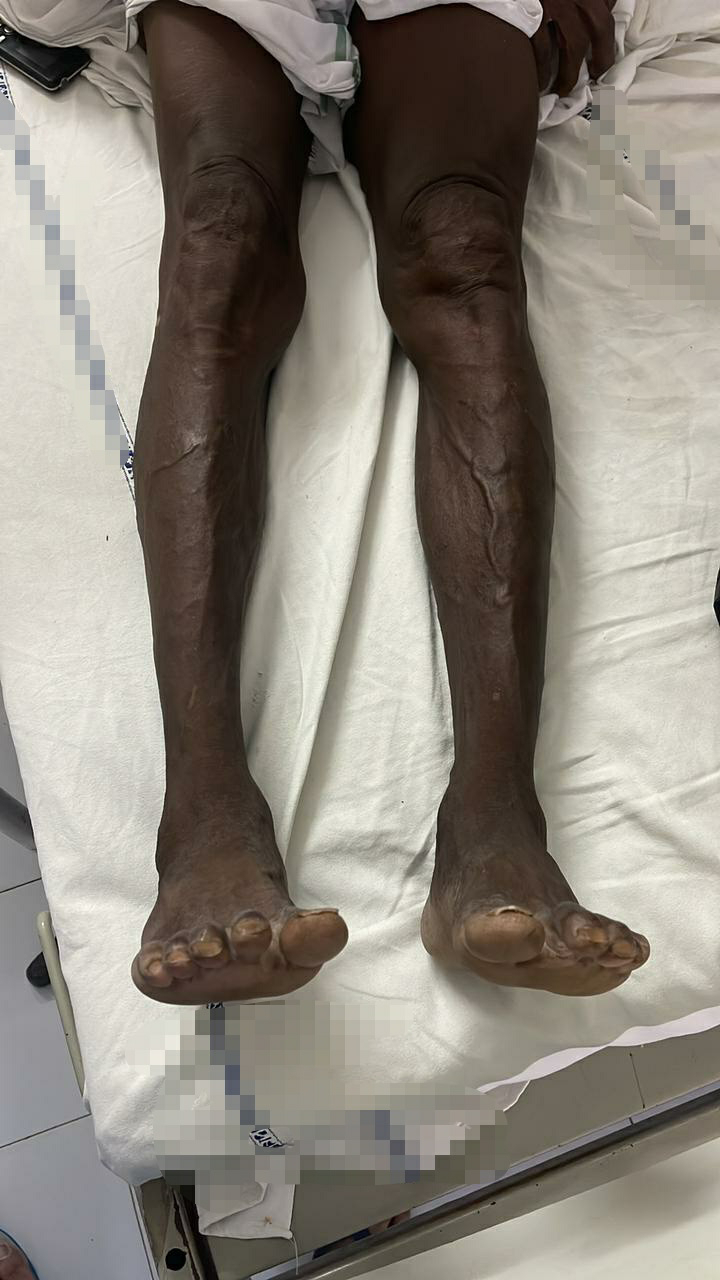
From the above CNS examination it is clearly understood that there is bilateral lower limb hypotonia,hyporeflexia and paraplegia characteristic of LMN LESION.
Other investigations
MRI OF BRAIN AND SPINAL CORD SHOWS FOLLOWING
There is significant enhancement which represents meningeal enhancement or exudates and following lesions in mri with multiple nodules in pulmonary apices suggest of pulmonary kochs and disseminated tuberculosis.
MRI spine
Mri images of the Brain

2.Vomitings
These are may be due to intracranial space occupying lesions which causes raised intracranial pressure and vomitings.
3.Gluteal abcess
Operated 5 months back
4.scrotal abcess
Operated 10days back
These two abcess are cold abcess as there is no signs of inflammation.
My suggestion to this is to do scraping of the abcess peripherally and send for culture to isolate the organism causing abcess.
1.ANATOMICAL LOCATION OF THE PROBLEM
FROM THE above investigations and reports the anatomical location of present paraparesis problem lies in the anterior right and left cerebral hemispheres, midline of falx cerebri and pyramidal tracts .
2.Possible etiology of PARAPARESIS
As the MRI suggests of disseminated tuberculosis and ring enhancing lesions in the brain.
The possible etiology might be spread of this mycobacterium from lumbosacral abcess to the blood vessels and from the blood vessels it reaches the circle of Willis in brain and further into anterior communicating artery occlusion
And further causing infarcts in pyramidal tracts causing Paraparesis.
3.POSSIBLE INVESTIGATIONS
as we are suspecting mycobacterium from MRI investigations we need to further confirm the organism
Best step is to isolate the organism
1-sputum microscopy
2-monteaux test
3-cbnaat
4-Bronchoscopy followed by bronchoalveolar lavage study
5-Culture of abcess fluid
Hence from the above investigations we can be able to confirm which type of mycobacterium it is and further treatment option is done.
4-Provisional Diagnosis from the case.
Paraparesis with L4,L5infective spondylodiscitis with left psoas abscess with ring enhancing lesions in right and left cerebral hemispheres with healing ulcer in right gluteal region secondary to drained gluteal abscess with pyocele left side operated ( 10 days back)
5- Therapeutic modality
1)T.ATT 3 tabs/day fdc
2)T.Benadon 40mg/od
3)T.pregabalin 75mg/po/h/s
4)OINT.MEGAHEAL FOR LOCAL APPLICATION
5)SITZ BATH WITH BETADINE TID
6)FREQUENT CHANGE OF POSITION
My thoughts on this CASE.
1) As the Patient is an autodriver with history of multiple sexual partners, a Hiv test named STARHS or RITA can help confirm diagnosing within 6months of infection
2) I prefer this hiv testing because both HIV AND TUBERCULOSIS are commonly associated together and thus if detected early antiretroviral therapy can also be started.
3)And a DW-MRI ( diffusion weighted MRI ) is further preferred because it helps in location of acute infarcts,tumours in brain as the patient had a history of sudden onset of paraplegia which may be due to vascular cause like stroke.
4)MR SPECTROSCOPY this confirms the tuberculoma by detecting increased levels of lipid lactate and cheesy material in brain
5) CT scan is also preferred Which clearly shows any edema in the brain,that MRI couldn't appreciate.
Thank you.





Comments